Formal Verification
Formal Verification
- Checks for all possible runs
- Advantages
–Provides 100% coverage for a defined property
–Complete verification of the specification is possible
–Good for state centric designs
- Disadvantages
–Limitations with the design sizes
Solution
Semiformal Verification
- Hybrid between formal verification and simulation
- Advantages
–Better coverage
–Can go deep into the design
–Can handle larger designs
- Disadvantages
–Suitable for finding bugs (falsification)
Three Variants of Formal Verification
Model checking
–Explicit
–Symbolic model checking (with BDD)
–Bounded model checking (with SAT: bmc)
Equivalence checking
–Equivalence checking is a process of comparing two circuits supposed to have identical behavior (verity, SixthSense, formality, conformal)
- Synthesis
- Retiming
- Power optimization
Theorem Proving
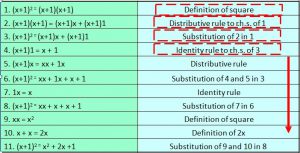
- Function to be proved: (x+1)(x+1) = x2 + 2x +1
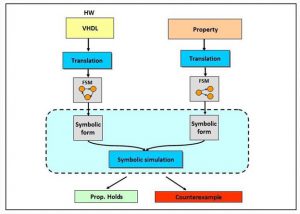
Model Checking – Tool Flow
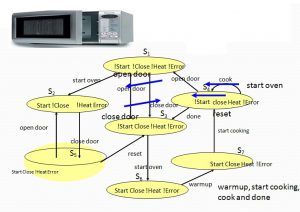
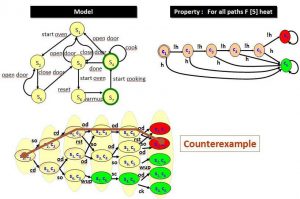
Microwave Oven Example
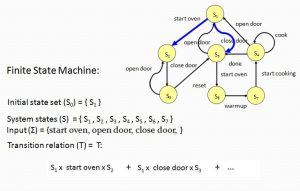
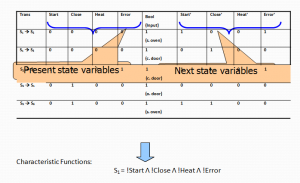
Symbolic Representation
Temporal Properties
Benefits of properties
- Improved understanding of system and its requirements
- Improved communication of design intent among involved parties
Any Time Brake implies slowdown
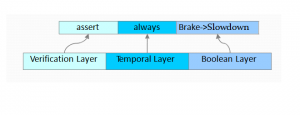
- Examples of temporal property description
–PSL (Property Specification Language)
–CTL (Computation tree logic)
–LTL (Linear time temporal logic)
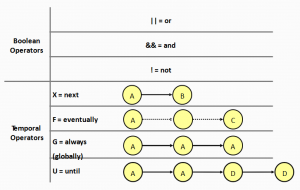
Temporal Logic – Syntax LTL
Model Checking – Schematic
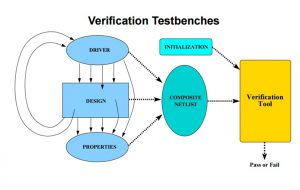
Testbenches
Truth Table and Boolean Decision Tree
BDD is a rooted, directed acyclic graph
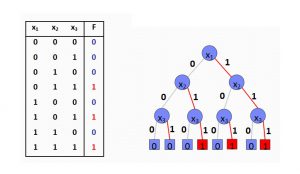
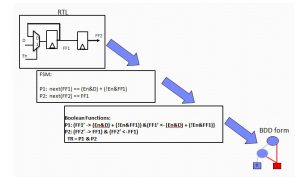
RTL to Boolean Functions/BDDs
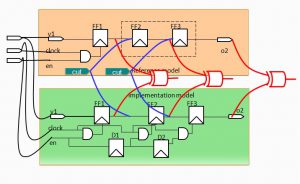
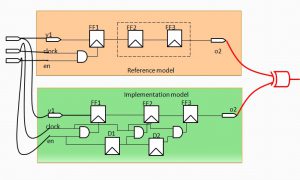
SEC – Top level Verification
SEC – Merge Point Verification
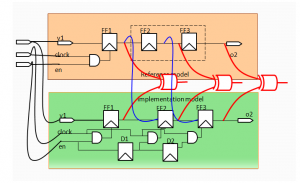
SEC – Cut Point Verification